Gandikota Quartzite Fm
Type Locality and Naming
Upper formation (3 of 3) of Chitravati Gr; although geochronological data has raised doubts on the inclusion of the Gandikota Quartzite within the Paleoproterozoic Chitravati Gr
Lithology and Thickness
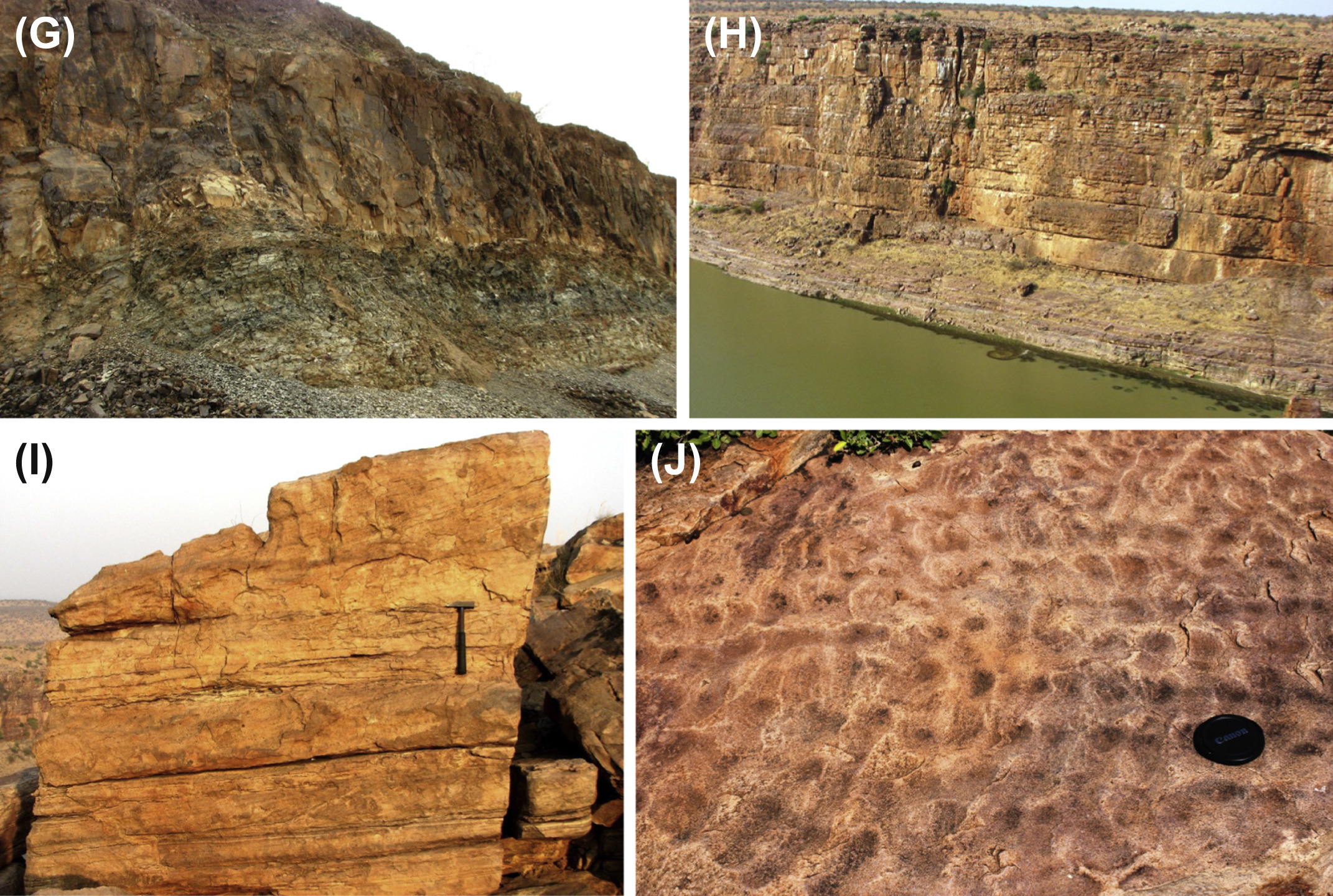
Quartzite, pebble beds. Amalgamated quartz arenite beds with sheet geometry (Fig. – image H). Medium- to coarse-grained quartz arenite to feldspathic arenite constitute the bulk of the formation. Large planar tabular to large trough cross-stratified units are intercalated with plane-parallel units and rippled units having straight or bifurcated crests, or interference ripples (Fig. – images I and J). Deformed cross-strata and ball-and-pillow structures are common in the upper part of the formation. Cross-stratified beds with opposite paleocurrent directions, hummocky cross-stratification and massive beds with local abundance of mud flakes occur throughout the Gandikota succession.
[Figures: Field photographs showing lithology and sedimentary features in the Chitravati Gr of the Cuddapah Supergroup. Tadpatri Fm - (G) shale with a thick mafic sill. Gandikota Quartzite Fm - (H) plateau forming sheet sandstone, (I) cross-stratified sandstone, and (J) interference ripples. (from Saha et al., 2016)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Overlies the Tadpatri Fm marls with a gradational contact.
Upper contact
Tectonic contact, then Bairenkonda Quartzite Fm (lower Nallamalai Gr)
Regional extent
GeoJSON
Fossils
Age
Depositional setting
Bar-interbar with tidal influence. Sediments were deposited primarily as high energy shallow wide bars and low energy interbars, which experienced frequent storms in open marine condition. On the whole, the Gandikota Quartzite represents subtidal to intertidal environment with well-preserved tidal flat showing frequent emergence of the depositional interface
Additional Information